Scientific American Supplement, No. 799, April 25, 1891 by Various, is part of the HackerNoon Books Series. You can jump to any chapter in this book here. THE RAISING OF THE ULUNDA.
THE RAISING OF THE ULUNDA.
Shortly after the recovery of the Ulunda, below described, the North American and West Indian squadron of the Royal Navy visited Halifax, Nova Scotia. The simple and novel means adopted for raising the ship attracted considerable attention among the officers of the fleet, and by way of stimulating the studies of the junior officers in this branch of their duties, a prize was offered for the best essay on the subject, to be competed for by the midshipmen of the various ships. The essays were adjudicated upon by Captain W.G. Stopford, of the flag ship—H.M.S. Bellerophon—and the first prize was awarded to the following paper, written by Mr. A. Gordon Smith, of H.M.S. Canada. The article needs no apology, but it is only just, says the Engineer, to mention the fact that the writer is not yet eighteen years of age.
The steamship Ulunda, on the remarkable raising and recovery of which this paper is written, is an iron screw ship of 1,161 tons, until lately belonging to the Furness line. It is a sister ship to the Damara, of the same company, and was built and engined by Alex. Stephens, shipbuilder and engineer, at Glasgow, being fitted with compound vertical engines, of 200 nominal horse power, having two cylinders of 33 inches and 66 inches diameter respectively, which are capable of sixty-five revolutions per minute, and give a speed of twelve knots an hour.
For supplying steam to the engines there are two return-tube boilers, each having three furnaces, and there is also a donkey boiler, which is used in harbor for working the four steam winches on deck.
She is divided into seven watertight compartments by athwartship bulkheads. The foremost one is the usual collision bulkhead. Between this and the foremost engine room bulkhead are Nos. 1 and 2 holds, separated by a watertight bulkhead. Abaft the after engine room are two more holds, divided in the same manner as the forward ones, and astern is another compartment, in which all stores are kept. Coal bunkers form a protection for the engines and boilers. Fore and aft the ship, as low down as possible, are a number of ballast tanks, which can be filled with or emptied of water as occasion requires to alter the trim of the ship. Extending over all holds there is a strong iron lower deck, about 8 feet below the upper deck, which is pierced with a hatch over each hold immediately under a corresponding hatch in the upper deck, for stowing and unstowing cargo.
In the engine room there are six steam pumps, two of them bilge pumps, worked by the main crossheads, for clearing the engine room of water. For pumping out the ballast tanks there are two more, which have their own independent engines. The remaining two are for various purposes. Besides these there are several hand pumps on the upper deck.
Having been built in 1885, the Ulunda is almost a new ship, and has been used principally as a cargo steamer, though she is provided also with a saloon and staterooms for a few passengers. She was on her way from St. John, New Brunswick, to Halifax, when during a thick fog she struck on Cowl Ledge, a reef between Bryer and Long Islands, on the southwest coast of Nova Scotia, about half a mile from the shore. The cause of the disaster was probably one of the strong tide eddies which exist in the Bay of Fundy, and which had set her in toward the shore. It was calm at the time, and she was making seven knots an hour; and, being close to the shore, leads should have been going in the chains. Had this precaution been taken, very probably she would have been able to stop or anchor in time to avert this catastrophe. There was no cargo on board, it being intended to ship one at Halifax for London.
When ashore on this reef she was sold by public auction at Halifax, and fell to a syndicate of private individuals for £440. These gentlemen at once decided to raise her if possible, transport her into dock, and repair her. They commissioned Captain Kelly, of the Princess Beatrice, a ship then in harbor, to visit her and see what could be done for that purpose. He went with a hired crew to Annapolis, and from thence proceeded to the steamer by means of a tug, a distance of about forty miles. When they arrived they found the Ulunda with her head to sea, and her stern in only 2 ft. of water at low tide, with a list of 30 deg. to port and her foremast broken short off. At high tide the water flowed over the upper deck. On examination, the engine room was found full of water, which did not rise and fall with the tide, showing that it had been filled at high tide through its skylight. No. 3 hold was also full, but had a slight leak, which was shown by the water falling slowly at low tide and rising in the same manner at high water. The other three holds were hopelessly leaky.
Upon investigation, it was decided to pump out the engine room compartment and No. 3 hold, and to make the iron lower deck watertight over the remaining holds. For this purpose three powerful pumps, with the necessary boilers, were obtained from Halifax, sent by rail to Annapolis, and then shipped on board a tug, from which they were hoisted into the Ulunda by means of the derricks on the mainmast. These were centrifugal pumps, capable of discharging 2,000 gallons a minute each. One was placed in the engine room, another with its suction in No. 3 hold, and when these two compartments were pumped dry, it was found that in No. 3 hold the leak was easily kept under, while in the engine room there was no leak at all. The third pump was not used.
In the two foremost holds 2,000 large casks were then placed, and all the hatches over the leaky holds—Nos. 1, 2, and 4—were battened down, and made airtight with felt, pitch, tow, etc. A small hole was then made in Nos. 1 and 2 hatches, about 2 ft. square. When the tide had sunk its farthest, these two holes were closed and made perfectly airtight, in the same manner as the hatches had been.
Before this took place the whole of the lower deck over the badly damaged holds had been prevented from bursting up by means of wooden shores, which were placed in rows about 4 ft. apart, and wedged firmly into position. The wood for the shores was obtained from Annapolis, and the casks from St. John. The ship went ashore on August 26, 1890. This work was commenced on September 8, and completed ten days afterward.
The labor of repairing her could only be carried out at low tide, and only then with the greatest difficulty, as the decks were very slippery with weeds, etc., and inclined at an angle of 30 deg. Everything was ready for floating her off at high tide on the 18th, and the hatches were closed up on that day.
She was raised off the rocks by the water rising and compressing the air in the two foremost holds, assisted by the buoyancy of the engine room and No. 3 compartments. At high water the bow was afloat, but she was aground by the stern. When, however, she was taken in tow by three tugs, she slowly slid down the reef and floated into deep water. One tug was placed on each bow, and the third was ahead. In this state she was towed into West Port, a distance of four miles, and there beached on a sheltered stretch of sand.
The casks performed no part in floating the ship off, but were only there in case the great pressure of air should cause the escape of some of it, in which event all the space underneath the lower deck would soon have been occupied with water instead of air. These casks would then, of course, have served to displace a large amount of this water, and so keep her afloat. Luckily the deck did not leak, and the barrels were thus not instrumental in the raising.
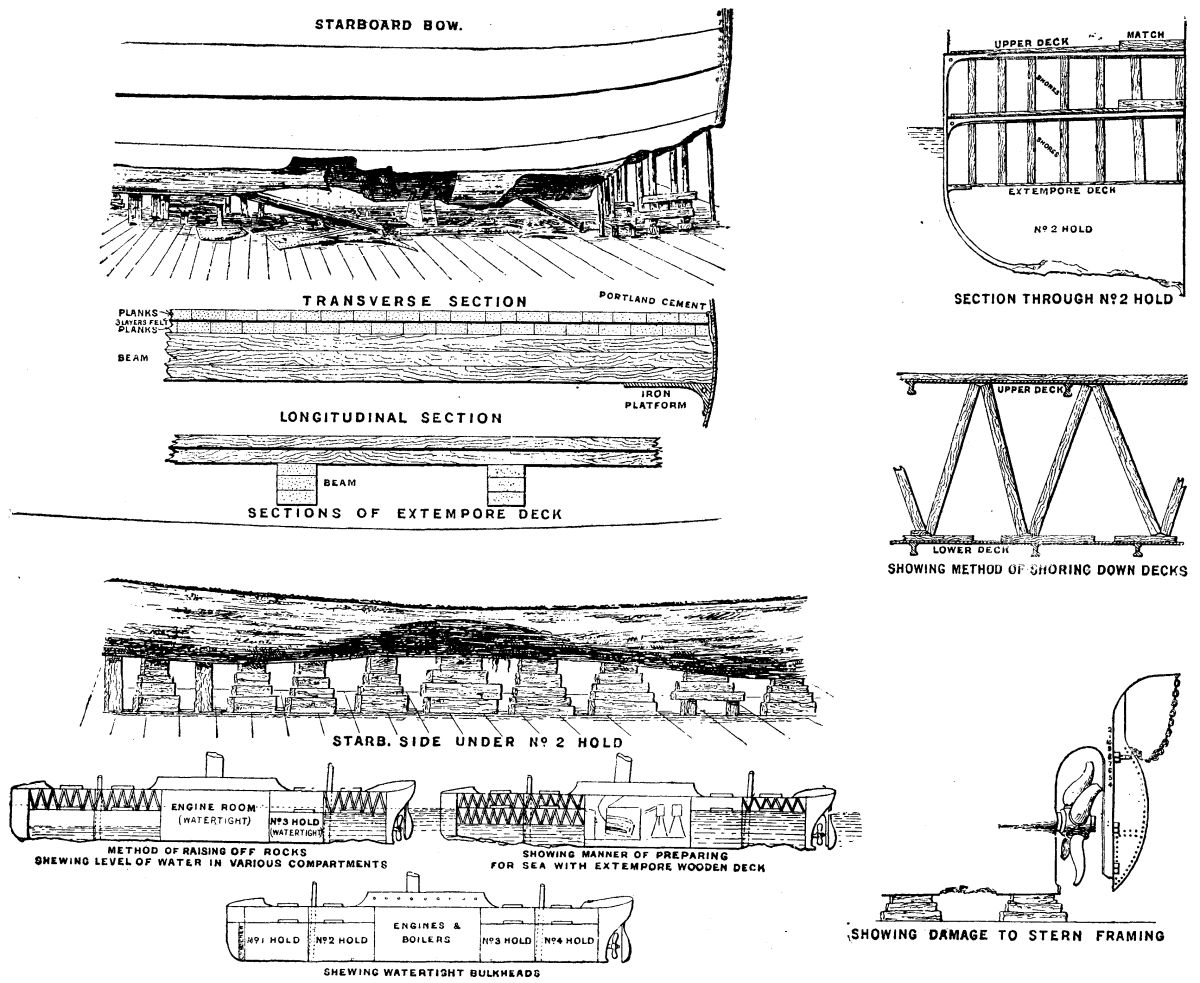
When beached the hatches were taken off, the casks removed, and a false deck was built about 7 ft. below the lower deck, and about 10 ft. above the keel. This was used as the bottom of the ship to take her round to Halifax, and was built in the following manner: A kind of iron platform, about 2 ft. wide, runs along the sides of the holds in the Ulunda for strengthening purposes, braced at intervals of 15 ft. by iron beams across the ship.
On this was built the wooden deck. Beams for this deck were constructed of three 3 in. planks, and were laid down on the iron platform about 3½ ft. apart, and firmly wedged into the ship's side. On these beams a layer of 3 in. planks was placed in a fore-and-aft direction and nailed down; on this were three layers of felt, and on this again more planks were laid down in the same direction as before.
The whole deck was then carefully calked and the sides made watertight with Portland cement. This deck only extended to the engine room bulkhead through the two foremost holds. It was prevented from bursting up by the pressure on the bottom of it, by means of shores, in the same manner as the iron deck had been served before. Shores were, therefore, connecting the three decks—the upper deck, lower deck, and wooden deck—this being done to equalize the pressure on the extemporé deck and the two permanent decks, and thus gain additional strength.
No deck was built in either of the after compartments, inasmuch as No. 3 hold was kept clear of water as before by its pump, and in No. 4 the deck was not necessary. To have built one there, as in the two foremost ones, although it would have given a little more reserve of buoyancy to the ship, would have raised the stern higher than the bows, and so would have increased the upward pressure on the wooden deck, and thus have increased the liability to burst up. For the same reason, when raising the ship off the rocks, no compressed air was used in the after hold to lift the ship. The anchors and cables were in both cases transferred aft, for the same purpose, namely, to diminish the upward pressure forward. In the case of the wooden deck leaking, 200 of the same casks were placed between it and the lower deck in the foremost hold to retain some of the buoyancy of the forepart, which would otherwise be lost. No decks were built in the compartment before the collision bulkhead, as very little buoyancy was lost by that space being full of water, and all that was there was confined to that compartment by the bulkhead and the iron lower deck.
While all these foregoing arrangements were being made for the exclusion of water from the inside of the ship, the engineers and firemen were employed clearing the engine room of some fifty tons of coal which had been washed from the open bunkers into the machinery by the sea, when the engine room was full and the ship on the reef. The greatest difficulty was experienced in digging out and excavating the engines from the coal and dirt, and still greater was the labor of cleaning all the mechanism and putting everything once more in an efficient steaming condition. But all was finished soon after the decks had been completed, and on October 12 she was ready for sea. On the following day she was floated off and started on her perilous voyage to Halifax, using her own engines, and making about five and a half knots an hour. Her steam pumps were by this time all ready for service to assist the big ones on deck in an emergency. She anchored once on her way round, at Shelburne, on the coast of Nova Scotia, arriving at Halifax at 1 p.m. on October 17. The trip round was a very anxious time for all hands, more especially when they were overtaken by a fresh gale in the Atlantic, for the forward deck was very liable to be burst up with the increased pressure on it caused by the pitching of the ship; also the rudder was entirely unable to bear any strain on it, because the lower part of the rudder post was unconnected with the stern post, part of the stern framing which connects the two having been broken off. Any heavy sea was therefore likely to carry away the rudder altogether, or the same accident might happen if the helm was put down too hard, rendering the ship unmanageable.
She was placed in dry dock as soon as she arrived at Halifax, and it was not until then that the full extent of the damages, caused by the pounding on the rocks, could be fully realized. The first 20 feet of the keel had been torn completely out, and about 30 feet from the stern there was an immense hole, with the thick plates torn and bent like paper, the framing and stanchions being twisted into all sorts of shapes almost beyond recognition. Under the foremast the bottom of the ship was bent up in the form of an arch, having been raised 4 feet above its natural position, with an immense hole punctured on the starboard side, besides several smaller ones. Also the aftermost 20 feet of keel was torn and jagged, with several small holes in the skin, and the lower portion of the stern framing was broken off, leaving the rudder post to hang down unsupported at its extremity. It would strike one on looking at these gaping wounds that it would be nearly impossible to place the Ulunda in an efficient condition again, but the work of renewing the damaged plates is being carried out at a great rate, and in three months' time it is hoped that all the repairs necessary will be completed and the ship once more doing her duty. She has already cost her owners some $10,000, and $40,000 are estimated to cover all future repairs.
The foremast was snapped off in a somewhat novel manner. She was pivoted on the rocks by her bows, and at high tide, the day after she struck, a breeze sprang up and turned her round; the tide sinking again, the whole weight of the ship came on the bottom of the ship where she was then touching, namely, just on the spot where the foremost was stepped, and right astern, leaving the center portion of the ship unsupported. This caused the foremast to rise, and it being held down by wire rigging, it snapped in several places, at the same time tearing up the shrouds from the deck. This accounts also for the arch-like bulge in the bottom at that spot and for the damages astern; also for the fact that Captain Kelly discovered the ship with her head to sea.
Another incident happened when the ship was just rising off the rocks, which nearly resulted in a catastrophe. When the ship was just beginning to lift, the leak in No. 3 compartment was found to be gaining on its pump. A diver was at once sent down to ascertain the cause, and he found that a small hole, about 6 inches square, had been punctured in the skin, which until then had been kept tight by the rock that had caused it. It was necessary to close this leak at once. An iron bolt, which was screwed for a nut at one end, was obtained and passed through a strong piece of wood about 2 feet square. The inside of this board was cushioned with canvas and oakum, and it was taken down outside the ship by the diver and placed over the hole, with the feathered end of the bolt sticking through the hole; the diver was then sent down inside the hold, and with a nut set up the whole cushion until the flow of water was stopped. The leak was thus stopped which had threatened the arrangements for floating the ship with failure.
It has been seen that the method of raising the Ulunda was very simple. She was floated off by the rising tide. If there had been only a small instead of an 18 foot rise, some other mode would have to have been adopted. No attempt was made to stop any of the leaks, except the one just stated, but a deck above the lacerations was made water-tight, and this, together with the sides of the ship hanging down, formed a kind of diving bell, the pressure of air in which, caused by the water outside, acting on this deck, being the principal means of buoying up the ship, assisted by the buoyancy of the two water-tight compartments. The deck afterward built was only necessary for the safety of the ship, she being able to float without it; but it would have been suicidal to trust the ship on the Atlantic in the state she was in when raised, since with any swell on, the compressed air would escape and its place be taken by water, the buoyancy necessary for keeping her afloat being thus lost.
It only remains to be said that the risks run in steaming around to Halifax by herself were, as it was, very great, and had the wind and sea been less favorable, the undertaking would probably have proved a disastrous failure.
About HackerNoon Book Series: We bring you the most important technical, scientific, and insightful public domain books.
This book is part of the public domain. Various (2004). Scientific American Supplement, No. 799, April 25, 1891. Urbana, Illinois: Project Gutenberg. Retrieved https://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/11649/pg11649-images.html
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org, located at https://www.gutenberg.org/policy/license.html.

